|
AMINOGUANIDINE
HYDROCHLORIDE
|
||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 79-17-4
(Base) 1937-19-5; 87667-21-8 (HCl) |
|
| EINECS NO. | 217-707-7 | |
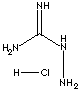
| FORMULA | H2NC(=NH)NHNH2·HCl | |
| MOL WT. | 110.55 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2925.20 | |
| TOXICITY | ||
| SYNONYMS |
Aminiguanidine
monohydrochloride; Pimagedine hydrochloride;
|
|
| Hydrazinecarboximidamide, monohydrochloride; Guanyl hydrazine Hydrochloride; Guanylhydrazine hydrochloride; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
white crystaline powder |
|
| MELTING POINT | 163 - 168 C | |
| BOILING POINT | >280 C (Decomposes) | |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.34 | |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Highly soluble | |
| pH |
|
|
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic. | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Guanidine,
also called carbamidine, is a strongly alkaline and
water-soluble
compound, NHC(NH2)2 It is formed in urine
as a normal product
of protein metabolism in the body by
the oxidation of guanine. Guanidine has imine group
and aminoacetal functional group in the small structure.
Aminoacetal (aminal) is the functional group which has two amine groups attached to the
same carbon atom. Imine is a compound containing the bivalent =NH group combined with a bivalent
nonacid group, as R-HC=NH. It is produced by the condensation reactions of
aldehydes or ketones with ammonia (or amines). Imino is a prefix denoting the
presence of the bivalent group =NH attached to nonacid radicals. Imine can reduced
and hydrolysed to prepare corresponding amines. Imine
is involved in Diels-Alder
reaction, Povarov reaction, Aza-Baylis-Hillman reaction and Eschweiler-Clarke reaction.
In industry, guanidine,
containing nitrogens and N=C solid bond, and its modified
derivatives are versatile intermediates used
in the manufacture of plastics, resins, rubber chemicals,
nitroguanidines (explosives), photo
chemicals, fungicides, and disinfectant. It has also
biotechnological application of protein separation,
purification and as a protein denaturant. It can be
used as an oxygen scavenger to prevent corrosion
damage. It is used as a component of rocket propellants
because it produce a large amount of heat
when burned.
Aminoguanidine is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyestuffs and other organic derivatives (photochemicals, explosives). It is used as a selective inhibitor of inducible nitric oxide synthase in biochemistry. |
||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystalline powder |
|
|
CONTENT |
98.0% min |
|
|
LOSS ON DRY |
2.0% max |
|
|
TRANSPORTATION |
||
| PACKING | 25kgs in bag | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 43-52/53, Safety Phrases: 24-28A-37-45 | ||